Today, the number of people with Diabetes are rising exponentially. Diabetes is a metabolic disease in which blood sugar/glucose levels are too high, also referred to as hyperglycemia. Diabetes is classified as: Type 1 diabetes where a person cannot produce hormone called insulin (that breaks down ingested sugar) in the body and need daily administration of insulin. Whereas in Type 2 diabetes a person can produce insulin but it is ineffective. These people take medications or even administer insulin to help maintain of daily blood sugar level. The third type is a Gestational diabetes occur during pregnancy where the blood sugar level is above the normal value.
People with diabetes are often asked to maintain their daily sugar intake, however, managing the sugar levels remains a major challenge in these patients, says Jigna Parekh, PharmD., MS, Senior Clinical Trial Manager at Incyte Corporation, USA. In order to prevent high sugar levels, some people tend to skip meals, while some tend to eat one or two big meals throughout the day and starve the rest of the time. In any scenario, body is deprived of major nutrients and can lead to hypoglycemia (low sugar levels), loss of energy, fall and sometimes hospitalizations in severe cases. And those people who do not manage sugar levels may end up with further complications of heart, skin, eye, diabetic ketoacidosis, kidney, mental distress and more.
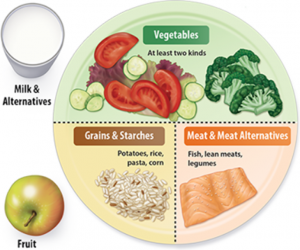
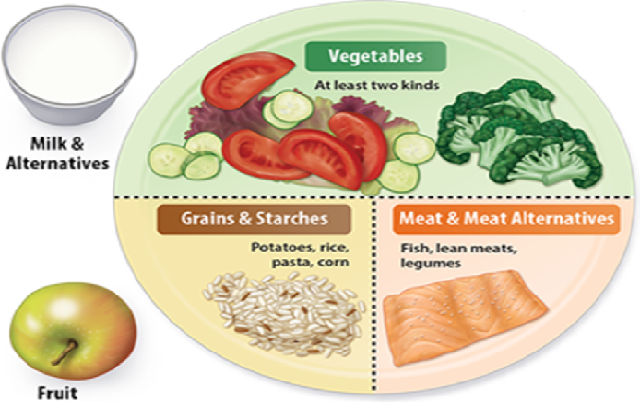
Dr. Parekh says, regardless of the type of diabetes day to day living with it is not easy, but it can be managed with some simple lifestyle modifications. One can begin with food; what to eat, how much to eat and when to eat can help manage diabetes. Eating small planned meals at a regular intervals and a healthy food choices can help. In addition, there are health apps available on smart phones that can help you track your daily weight, calorie intake and exercise. These has benefited lot of people with diabetes worldwide. But there still remains some confusion around ‘what do you mean by eating “well-balanced” meals?’ To answer this let’s talk about the daily calorie goal of a normal individual, which is – Carbohydrate 50%, Fat 30% and Protein 20% along with vegetables and fruits. This daily calorie goal should be divided over four to five meals such as breakfast, snack, lunch, snack 2 (optional) and dinner. So now let us see how to calculate this. Say for example, if daily calorie goal is 1000 Kcal. For a normal individual it will be, carbohydrate of 500 Kcal, Fat of 300 Kcal and Protein of 200 Kcal. This individual content is divided over four to five meals depending on individual preference. To put all these calculations in real life, one can follow ‘plate method’ a guide to plan meals showed in the picture. Please note, for a person with diabetes, the carbohydrate goal may vary depending on their blood sugar levels. And for the same individual, the protein and fat content is adjusted to meet that daily calorie goal.

Maintaining a healthy body weight is equally important. If an individual is overweight then physical exercise of at least 30 – 45 minutes three to four times a week is advisable. Moderate-intensity exercise, stretching, yoga, aerobics, walking, weight lifting with light weights may be beneficial. In general, irrespective of overweight or diabetes, exercising few days a week is healthy way of living, adds Dr. Parekh.
It is equally important to follow proper medication regimen as prescribed by the physician. People with type 1 diabetes take insulin. Whereas in type 2 diabetes, depending on their blood sugar level some individual manage their diabetes just with eating right and exercising, while some are given prescribed oral medication with or without insulin.
Likewise, the annual physical examination including visit to health care physician (for overall health checkup, blood sugar levels, cholesterol, blood pressure), dentist (to detect gum disease), podiatrist (for foot health), ophthalmologists (to detect high pressure, changes in the retina and prevent blindness) is favorable.
Dr. Parekh says to be aware of the signs and symptoms for hypoglycemia which is low blood sugar levels. This may vary from person to person. Common signs and symptoms includes sweating, chills, nervousness, feeling week, fast heartbeat, headache, hunger. Occasionally people do not pay attention to the signs and end up hospital due to loss of consciousness or fall and injury. The best way to treat this is ‘15-15 Rule’. Have 15 gram carbohydrate (in form of glucose tablets, gel, ½ cup of juice, 1 tablespoon of sugar or honey or hard candies) to raise blood sugar, check your sugar levels after 15 minutes. If there is no change, then have another serving. If there is severe episode of hypoglycemia and the 15-15 rule isn’t working then time to go to hospital emergency for immediate treatment, waste no time.
Lastly, there is no cure to diabetes and millions of people are living with it. Accepting and empowering it is the way to manage it, says, Dr. Parekh.
Jigna Parekh, PharmD., MS